Archive for the ‘Central Cord Syndrome’ Category
Central Cord Syndrome
Central Cord Syndrome (CCS) is an incomplete injury to the cervical cord resulting in more extensive motor weakness in the upper extremities than the lower extremities. The mechanism of injury occurs from a hyperextension injury with pre-existent osteophytic (abnormal bony outgrowth) spurs, without damage to the vertebral column.
Mechanism and Causes of Injury
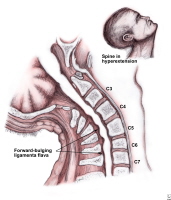
CCS occurs typically in patients with hyperextension injuries where the spinal cord is squeezed or pinched between anterior cervical spondylotic bone spurs and the posterior intraspinal canal ligament, the ligamentum flavum. The ligamentum flavum is a strong ligament that connects the laminae of the vertebrae. It serves to protect the neural elements and the spinal cord and stabilize the spine so that excessive motion between the vertebral bodies does not occur.
The injury occurs as a result of anterior and posterior compression of the spinal cord, leading to edema, hemorrhage or ischemia to the central portion of the spinal cord. The site of most injuries is in the mid-to-lower cervical cord. Due to the anatomical lamination of the corticospinal tract with the arm fibers medially, and the leg fibers laterally, the arms are affected more so than the legs, resulting in a disproportionate motor impairment.
Symptoms
Patients are typically left with motor weakness of the upper extremities and lesser involvement of the lower extremities. A varying degree of sensory loss below the level of the lesion and bladder symptoms (urinary retention) may both occur.
Incidence
This syndrome more commonly affects patients age 50 and older who have sustained a cervical hyperextension injury.
CCS may occur in patients of any age and is seen in athletes who present with not only hyperextension injuries to their neck but associated ruptured disc(s) with anterior cord compression.
CCS affects males more frequently than females.
Diagnosis
Evaluation of the patient includes a complete history, a thorough neurological exam, MRI and CT of the cervical spine, and cervical spine x-rays including supervised flexion and extension x-rays.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A diagnostic test that produces three-dimensional images of body structures using powerful magnets and computer technology; can show direct evidence of spinal cord impingement from bone, disc, or hematoma.
- Computed tomography scan (CT or CAT scan): A diagnostic image created after a computer reads x-rays; can show the shape and size of the spinal canal, its contents, and the structures around it.
- X-ray: Application of radiation to produce a film or picture of a part of the body can show the structure of the vertebrae and the outline of the joints. X-rays of the spine delineate fractures and dislocations, as well as the degree and extent of spondylitic changes. Flexion/extension views assist in evaluation of ligamentous stability.
Surgical Treatment
Acute surgical intervention is not usually necessary unless there is significant cord compression. Prior to the CT-MRI era, surgical intervention was thought to be more harmful because of the risk of injuring a swollen cervical cord and worsening the deficit. However, with advanced imaging technology such as CT and MRI, patients with compression of the spinal cord secondary to traumatic herniated discs and other lesions can be quickly diagnosed and surgically decompressed. In cases with anterior bony ridges and spinal canal narrowing secondary to ligamentous thickening and or stenosis, acute surgery is usually not performed until the patient has made maximum recovery. Reassessment at that time may lead to surgery depending on the underlying cause. If there is significant motor weakness after a period of recovery, or neurological deterioration or spinal instability, then surgical intervention may be considered.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment consists of immobilization of the neck with a cervical orthosis, steroids unless contraindicated, and rehabilitation with physical and occupational therapy.
Outcome
Many patients with CCS make spontaneous recovery of motor function while others experience considerable recovery in the first six weeks post injury.
If the underlying cause is edema, recovery may occur relatively soon after an initial phase of motor paralysis or pareses. Leg function usually returns first, followed by bladder control and then arm function. Hand movement and finger dexterity improves last. If the central lesion is caused by hemorrhage or ischemia, then recovery is less likely and the prognosis is more devastating.
The prognosis for CCS in younger patients is favorable. Within a short time, a majority of younger patients recover and regain the ability to ambulate and perform daily living activities. However, in elderly patients the prognosis is not as favorable, with or without surgical intervention.
Become Pain Free | Pain Specialist in Texas
Call Us: (214) 396-3647 | (888) 373-3720 Fax #: (888 )238-9155 | E-mail Us