Posts Tagged ‘Neurosurgery’
The 5 things you should know about chronic pain from BecomePainFree.com
Only sufferers of chronic pain know the implications of pain in every aspect of life. Family members and friends of someone with chronic pain may sympathize to some extent, but it’s difficult to truly understand how chronic pain affects someone. If you have a friend or family member suffering from chronic pain — whether caused by an accident or injury, or another health condition such asfibromyalgia — use these tips to understanding chronic pain to help you be most supportive to your loved one.
1.Don’t pass chronic pain off as “all in your head.” People who suffer from chronic pain are rarely fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. Conditions causing chronic pain can make an individual truly miserable. Many cases of chronic pain are difficult to diagnose, and thus management and treatment is far more challenging than in cases of acute pain, where the source of pain is easily diagnosed.
2.Chronic pain is different from acute pain. Acute pain lasts for a brief period of time, perhaps following an injury or accident. Chronic pain, on the other hand, is persistent and can even be permanent. We have all felt acute pain at some point in time, but only those with chronic pain know what it is to be in pain constantly.
3.Chronic pain may be caused by or the cause of other health conditions. Difficulty sleeping and depression are two conditions that often plague sufferers of chronic pain. Chronic pain can create a vicious cycle for the sufferer, for example: chronic pain leads to sleep disturbances, whereas lack of sleep can exacerbate chronic pain. The same is true of depression; it can be caused by or the cause of some chronic pain symptoms.
4.Every person’s pain is different. We all experience and express pain differently. Some people may be more tolerant of pain in specific parts of the body, while other people may express discomfort with pain in the same area or caused by the same condition.
5.Chronic pain is emotionally exhausting. Imagine that you are in pain or don’t feel good for months or years on end, with no relief. Constant pain wears on the emotions and can lead to depression and anger. Treatment for chronic pain often means treating each symptom and effect of that pain, including mental health issues such as depression.
Chronic pain is a lonely condition. If someone you know or love is suffering from chronic pain, don’t try to compare their pain to your own experiences, or assume their pain is all made up. Rather, offer your care and support. Be willing to listen when they need to talk and supportive throughout treatment programs.
Call Us: (214) 396-3647 | (888) 373-3720 Fax #: (888 )238-9155 | E-mail Us
Adult Stem Cell Therapy to Treat Back Pain, Stem Cell, Spine Stem Cells, Stem Cell Treatment
Adult Stem Cell Therapy that doesn’t require FDA approval to treat lumbar and cervical spine conditions resulting from injury or aging, and is also involved with an FDA clinical trial investigating the use of Adult Stem Cells.
These stem cells are autologous – they are taken from an adult patient and returned to that same patient in a concentrated form to the damaged area in a 30-minute procedure. This type of adult stem cell therapy does not require FDA approval to administer.
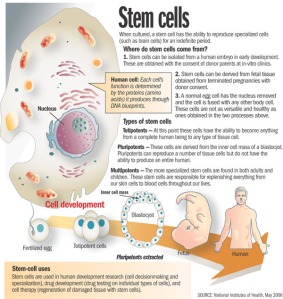
When it comes to stem cells, there is often a lot of mystique surrounding them. We hear from the media that we can create a human being out of a bundle of cells, which is not necessarily true. We also tend to look at embryonic stem cells as being the only type of stem cell. With these types of embryonic stem cells, one idea is to be able to create a liver or kidney in a Petri dish, which is not controllable or feasible at this point, and the work being done by the BecomePainFree.com medical group.
When we look at stem cell types, we have embryonic stem cells on one hand and adult stem cells on the other. The characteristics of each of these are not like other cells. For instance, a liver cell can divide but it will only ever be a liver cell. These stem cells, both embryonic and adult, can turn into different types of cells. The embryonic stem cells can really turn into any cell type, but adult stem cells are limited as far as the cells they can turn into. This depends upon environment or niche and what they are already programmed to become. A lot of people think there is a lot of promise with embryonic stem cells and there is, although we are not quite there yet.
We are still at the forefront of stem cell technology and embryonic stem cells in particular. With those cells, we do not have the ability to control what types of tissue they turn into. For example, we could be trying to manipulate these cells to turn into kidneys, but they might start to develop as pancreatic cells, which is troublesome. Another key with all stem cells is that they can proliferate quite a bit, usually at a higher rate than just a regular somatic cell. Although this sounds good at first glance, the issue with this, particularly with embryonic stem cells, is we cannot control that division. Hence, these cells can keep going and going without dying. In the normal bodily process, cells are programmed to die after a certain time, but these embryonic stem cells can evade that action and continue dividing, which takes on the characteristic of cancer cells. In some animal studies, an issue that keeps arising is development of tumors in some of these animals. It is difficult to predict if tumors are going to form when using some sort of embryonic stem cell treatment. This is still a scary area through which we are still trying to navigate.
However, the focus of the BecomePainFree.com medical group is on adult mesenchymal stem cells. On the whole, the media does not give a lot of attention to these kinds of stem cells, as using them avoids any kind of ethical or controversial issues. There is a great amount of research being done on adult mesenchymal stem cells, however, because they are very powerful.
First off, we can control what cell type they turn into much more easily. For example, the treatment used by the BecomePainFree.com medical group focuses on Mesenchymal precursor cells (MPC). Mesenchymal means these cells are not going to turn into any kind of blood product such as a red blood cell or white blood cell, although they are derived from bone marrow. The fact that they are precursor cells means these MPCs are only going to differentiate into one of a few cell types. They are either going to become bone cells, i.e., osteoblasts, or chondrocytes, i.e., cartilaginous tissue such that we see in intervertebral discs and joints, etc. All of that really depends on the environment in which we place these adult stem cells where it is well suited to do this. For example, we can inject these MPCs into a bone fracture, and because the cells are surrounded by bone tissue, these cells will receive signals from the surrounding cells that tell them to turn into bone. However, the cells we use will be injected into a disc or joint, and the cells composing the disc and joint tissue will signal the stem cells to develop into similar tissue. Again, there is no chance of any sort of pancreatic cell or nerve cell type spontaneously forming because we are using certain adult stem cell types, which are limited and cannot turn into anything like that. In addition, as the tissue surrounding the disc and joint is relatively avascular, there is not really any worry of these cells migrating through the blood stream to somewhere else in the body and causing any sort of problem. As far as the proliferation issue with embryonic stem cells, we have not seen this issue with adult stem cells in terms of dividing exponentially without ceasing. There is almost a preset limit to how many times these adult stem cells will divide.
Become Pain Free | Pain Specialist in Texas
Call Us: (214) 396-3647 | (888) 373-3720 Fax #: (888 )238-9155 | E-mail Us https://www.becomepainfree.com/
Confusion about Spinal Fusion, Spine Fusion, Spine Fusion Surgery, Back Fusion Surgery, Back Surgery
Spinal Fusion is used to treat spinal instability and alleviate chronic mechanical back pain but many people are unsure of what spinal fusion actually does. Spinal fusion is surgery to permanently connect two or more vertebrae in your spine, eliminating motion between them.
Spinal fusion involves many techniques designed to mimic the normal healing process of broken bones. During spinal fusion, your surgeon places bone or a bone-like material within the space between two spinal vertebrae. Metal plates, screws and rods may be used to hold the vertebrae all together, so they can heal into one solid unit.
Because spinal fusion surgery immobilizes parts of your spine, it changes the way your spine can move. This places additional stress and strain on the vertebrae above and below the fused portion, and may increase the rate at which those areas of your spine degenerate.
BecomePainFree.com can help
Become Pain Free | Pain Specialist in Texas
Call Us: (214) 396-3647 | (888) 373-3720 Fax #: (888 )238-9155 | E-mail Us
Anterior cervical discectomy & fusion (ACDF), ACDF, ACDF Spine Surgery
 ACDF Spine/Back Surgery Overview
ACDF Spine/Back Surgery Overview
Come see on of our Doctors today please visit https://www.becomepainfree.com/
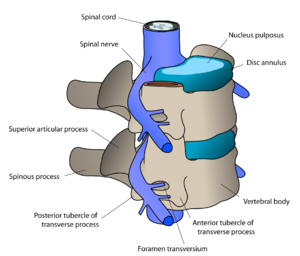
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a surgical procedure performed to remove a herniated or degenerative disc (Fig. 1) in the cervical (neck) spine. The surgeon approaches the spine from the front, through the throat area. After the disc is removed, the vertebrae above and below the disc space are fused together. Your doctor may recommend a discectomy if physical therapy or medication fail to relieve your neck or arm pain caused by inflamed and compressed spinal nerves. Patients typically go home the same day; recovery time takes 4 to 6 weeks.
Figure 1, top. (top view of vertebra) Degenerative disc disease causes the discs (purple) to dry out. Tears in the disc annulus can allow the gel-filled nucleus material to escape and compress the spinal cord causing numbness and weakness. Bone spurs may develop which can lead to a narrowing of the nerve root canal (foraminal stenosis). The pinched spinal nerve becomes swollen and painful.
What is an anterior cervical discectomy & fusion (ACDF)?
Discectomy literally means “cutting out the disc.” A discectomy can be performed anywhere along the spine from the neck (cervical) to the low back (lumbar). The surgeon reaches the damaged disc from the front (anterior) of the spine — through the throat area. By moving aside the neck muscles, trachea, and esophagus, the disc and bony vertebrae are accessed. In the neck area of the spine, an anterior approach is more convenient than a posterior (back) because the disc can be reached without disturbing the spinal cord, spinal nerves, and the strong neck muscles of the back. Depending on your particular case, one disc (single-level) or more (multi-level) may be removed.
After the disc is removed, the space between the bony vertebrae is empty. To prevent the vertebrae from collapsing and rubbing together, the surgeon fills the open disc space with a bone graft. The graft serves as a bridge between the two vertebrae to create a spinal fusion. The bone graft and vertebrae are often immobilized and held together with metal plates and screws. Following surgery the body begins its natural healing process and new bone cells are formed around the graft. After 3 to 6 months, the bone graft should join the vertebrae above and below to form one solid piece of bone. With instrumentation and fusion working together, the bone may actually grow around the plates and screws – similar to reinforced concrete.
Bone grafts come from many sources. Each type has advantages and disadvantages.
- Autograft bone comes from you. The surgeon takes your own bone cells from the hip (iliac crest). This graft has a higher rate of fusion because it has bone-growing cells and proteins. The disadvantage is the pain in your hipbone after surgery. Harvesting a bone graft from your hip is done at the same time as the spine surgery. The harvested bone is about a half inch thick – the entire thickness of bone is not removed, just the top half layer.
- Allograft bone comes from a donor (cadaver). Bone-bank bone is collected from people who have agreed to donate their organs after they die. This graft does not have bone-growing cells or proteins, yet it is readily available and eliminates the need to harvest bone from your hip. Allograft is shaped like a doughnut and the center is packed with shavings of living bone tissue taken from your spine during surgery.
- Bone graft substitute comes from man-made plastic, ceramic, or bioresorbable compounds. Often called cages, this graft material is packed with shavings of living bone tissue taken from your spine during surgery.
After fusion you may notice some range of motion loss, but this varies according to neck mobility before surgery and the number of levels fused. If only one level is fused, you may have similar or even better range of motion than before surgery. If more than two levels are fused, you may notice limits in turning your head and looking up and down. New motion-preserving artificial disc replacements have emerged as an alternative to fusion. Similar to knee replacement, the artificial disc is inserted into the damaged joint space and preserves motion, whereas fusion eliminates motion. Outcomes for artificial disc compared to ACDF (the gold standard) are similar, but long-term results of motion preservation and adjacent level disease are not yet proven. Talk with your surgeon about whether ACDF or artificial disc replacement is most appropriate for your specific case.
Who is a candidate?
You may be a candidate for discectomy if you have:
- diagnostic tests (MRI, CT, myelogram) show that you have a herniated or degenerative disc
- significant weakness in your hand or arm
- arm pain worse than neck pain
- symptoms that have not improved with physical therapy or medication
ACDF may be helpful in treating the following conditions:
- Bulging and herniated disc: The gel-like material within the disc can bulge or rupture through a weak area in the surrounding wall (annulus). Irritation and swelling occurs when this material squeezes out and painfully presses on a nerve.
- Degenerative disc disease: As discs naturally wear out, bone spurs form and the facet joints inflame. The discs dry out and shrink, losing their flexibility and cushioning properties. The disc spaces get smaller. These changes lead to foraminal or central stenosis or disc herniation (Fig. 1).
The surgical decision
Most herniated discs heal after a few months of nonsurgical treatment. Your doctor may recommend treatment options, but only you can decide whether surgery is right for you. Be sure to consider all the risks and benefits before making your decision. Only 10% of people with herniated disc problems have enough pain after 6 weeks of nonsurgical treatment to consider surgery.
Your surgeon will also discuss the risks and benefits of different types of bone graft material. Autograft is the gold standard for rapid healing and fusion, but the graft harvest can be painful and at times lead to complications. Autograft is more commonly used these days as it has proven to be as effective for routine 1 and 2 level fusions in non-smokers.
Who performs the procedure?
A neurosurgeon or an orthopedic surgeon can perform spine surgery. Many spine surgeons have specialized training in complex spine surgery. Ask your surgeon about their training, especially if your case is complex or you’ve had more than one spinal surgery.
What happens before surgery?
You may be scheduled for presurgical tests (e.g., blood test, electrocardiogram, chest X-ray) several days before surgery. In the doctor’s office, you will sign consent and other forms so that the surgeon knows your medical history (allergies, medicines/vitamins, bleeding history, anesthesia reactions, previous surgeries). Discuss all medications (prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal supplements) you are taking with your health care provider. Some medications need to be continued or stopped the day of surgery.
Stop taking all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (Naprosyn, Advil, Motrin, Nuprin, Aleve, etc.) and blood thinners (Coumadin, Plavix, etc.) 1 to 2 weeks before surgery as directed by the doctor. Additionally, stop smoking, chewing tobacco, and drinking alcohol 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery because these activities can cause bleeding problems. No food or drink is permitted past midnight the night before surgery.
Smoking
The most important thing you can do to ensure the success of your spinal surgery is quit smoking. This includes cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, and smokeless tobacco (snuff, dip). Nicotine prevents bone growth and puts you at higher risk for a failed fusion. Patients who smoked had failed fusions in up to 40% of cases, compared to only 8% among non-smokers [1]. Smoking also decreases your blood circulation, resulting in slower wound healing and an increased risk of infection. Talk with your doctor about ways to help you quit smoking: nicotine replacements, pills without nicotine (Wellbutrin, Chantix), and tobacco counseling programs.
Morning of surgery
- Shower using antibacterial soap. Dress in freshly washed, loose-fitting clothing.
- Wear flat-heeled shoes with closed backs.
- If you have instructions to take regular medication the morning of surgery, do so with small sips of water.
- Remove make-up, hairpins, contacts, body piercings, nail polish, etc.
- Leave all valuables and jewelry at home (including wedding bands).
- Bring a list of medications (prescriptions, over-the-counter, and herbal supplements) with dosages and the times of day usually taken.
- Bring a list of allergies to medication or foods.
Arrive at the hospital 2 hours before (surgery center 1 hour before) your scheduled surgery time to complete the necessary paperwork and pre-procedure work-ups. An anesthesiologist will talk with you and explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks. An intravenous (IV) line will be placed in your arm.
What happens during surgery?
There are seven steps to the procedure. The operation generally takes 1 to 3 hours.
Step 1: prepare the patient
You will lie on your back on the operative table and be given anesthesia. Once asleep, your neck area is cleansed and prepped. If a fusion is planned and your own bone will be used, the hip area is also prepped to obtain a bone graft. If a donor bone will be used, the hip incision is unnecessary.
Step 2: make an incision
A 2-inch skin incision is made on the right or left side of your neck (Fig. 2). The surgeon makes a tunnel to the spine by moving aside muscles in your neck and retracting the trachea, esophagus, and arteries. Finally, the muscles that support the front of the spine are lifted and held aside so the surgeon can clearly see the bony vertebrae and discs.
Figure 2. A 2-inch skin incision is made on the side of your neck.
Step 3: prepare to remove disc
With the aid of a fluoroscope (a special X-ray), the surgeon passes a thin needle into the disc to locate the affected vertebra and disc.
To remove the damaged disc, the vertebrae above and below the disc must be held apart. Your surgeon first inserts a spreader into the body of each vertebra above and below the disc to be removed. Gentle tension is placed on the spreader to separate the two vertebrae.
Step 4: remove the disc fragments
The outer wall of the disc (annulus) is cut (Fig. 3). The surgeon removes about 2/3 of your disc using small grasping tools, and then looks through a surgical microscope to remove the rest of the disc. The posterior longitudinal ligament, which runs behind the vertebrae, is removed to reach the spinal canal. Any disc material pressing on the spinal nerves is removed.
Figure 3. The muscles are retracted to expose the vertebra. The disc annulus is cut open and the disc material is removed with grasping tools.
Step 5: decompress the nerve
Bone spurs (osteophytes) that press on your nerve root are removed. The foramen, through which the spinal nerve exits, is enlarged with a drill (Fig. 4). This procedure, called a foraminotomy, gives your nerves more room to exit the spinal canal.
Figure 4. (top view) The disc annulus and nucleus are removed to decompress the spinal cord and nerve root. Bone spurs are removed and the spinal foramen is enlarged to free the nerve.
Step 6. prepare a bone graft fusion
Using a drill, the open disc space is prepared on the top and bottom by removing the outer cortical layer of bone to expose the blood-rich cancellous bone inside. This “bed” will hold the bone graft material that you and your surgeon selected:
- Bone graft from your hip. A skin and muscle incision is made over the crest of your hipbone. Next, a chisel is used to cut through the hard outer layer (cortical bone) to the inner layer (cancellous bone). The inner layer contains the bone-growing cells and proteins. The bone graft is then shaped and placed into the “bed” between the vertebrae (Fig. 5).
- Bone bank or fusion cage. A cadaver bone graft or bioplastic cage is filled with the leftover bone shavings containing bone-growing cells and proteins. The graft is then tapped into the shelf space.
Figure 5. (side view) A bone graft (blue) is shaped and inserted into the shelf space between the vertebrae.
The surgeon may reinforce the bone graft with a metal plate screwed into the vertebrae to provide stability during fusion – and possibly a better fusion rate. An x-ray is taken to verify the position of the bone graft and the metal plate and screws (Fig. 6).
Come see on of our Doctors today please visit https://www.becomepainfree.com/
New option: artificial disc replacement. Instead of a bone graft or fusion cage, an artificial disc device is inserted into the empty disc space. In select patients, it may be beneficial to preserve motion. Talk to your doctor – not all insurance companies will pay for this new technology and out-of-pocket expenses may be incurred.
Step 7. close the incision
The spreader and retractors are removed. The muscle and skin incisions are sewn together with sutures. Steri-Strips or biologic glue is placed across the incision.
What happens after surgery?
You will awaken in the postoperative recovery area, called the PACU. Blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration will be monitored. Any pain will be addressed. Once awake, you will be moved to a regular room where you’ll increase your activity level (sitting in a chair, walking). Patients who have had bone graft taken from their hip may feel more discomfort in their hip than neck incision. Most patients having a 1 or 2 level ACDF are sent home the same day. However, if medical complications such as difficulty breathing or unstable blood pressure develop, you may need to stay overnight. You will be given written instructions to follow when you go home.
Discharge instructions
Discomfort
- After surgery, pain is managed with narcotic medication. Because narcotic pain pills are addictive, they are used for a limited period (2 to 4 weeks). As their regular use can cause constipation, drink lots of water and eat high fiber foods. Laxatives (e.g., Dulcolax, Senokot, Milk of Magnesia) can be bought without a prescription. Thereafter, pain is managed with acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol).
- Hoarseness, sore throat, or difficulty swallowing may occur in some patients and should not be cause for alarm. These symptoms usually resolve in 1 to 4 weeks.
Restrictions
- If you had a fusion, do not use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (e.g., aspirin; ibuprofen, Advil, Motrin, Nuprin; naproxen sodium, Aleve) for 6 months after surgery. NSAIDs may cause bleeding and interfere with bone healing.
- Do not smoke. Smoking delays healing by increasing the risk of complications (e.g., infection) and inhibits the bones’ ability to fuse.
- Do not drive for 2 to 4 weeks after surgery or until discussed with your surgeon.
- Avoid sitting for long periods of time.
- Avoid bending your head forward or backward.
- Do not lift anything heavier than 5 pounds (e.g., gallon of milk).
- Housework and yard-work are not permitted until the first follow-up office visit. This includes gardening, mowing, vacuuming, ironing, and loading/unloading the dishwasher, washer, or dryer.
- Postpone sexual activity until your follow-up appointment unless your surgeon specifies otherwise.
Activity
- You may need help with daily activities (e.g., dressing, bathing), but most patients are able to care for themselves right away.
- Gradually return to your normal activities. Walking is encouraged; start with a short distance and gradually increase to 1 to 2 miles daily. A physical therapy program may be recommended.
- If applicable, know how to wear a cervical collar before leaving the hospital. Wear it when walking or riding in a car.
Bathing/Incision Care
- You may shower 1 to 4 days after surgery. Follow your surgeon’s specific instructions. No tub baths, hot tubs, or swimming pools until your health care provider says it’s safe to do so.
- If you have staples or stitches when you go home, they will need to be removed. Ask your surgeon or call the office to find out when.
When to Call Your Doctor
- If your temperature exceeds 101° F, or if the incision begins to separate or show signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, or drainage.
- If your swallowing problems interfere with your ability to breathe or drink water.
Recovery and prevention
Schedule a follow-up appointment with your surgeon for 2 weeks after surgery. Recovery time generally lasts 4 to 6 weeks. X-rays may be taken after several weeks to verify that fusion is occurring. The surgeon will decide when to release you back to work at your follow-up visit.
A cervical collar or brace is sometimes worn during recovery to provide support and limit motion while your neck heals or fuses (see Braces & Orthotics). Your doctor may prescribe neck stretches and exercises or physical therapy once your neck has healed.
If you had a bone graft taken from your hip, you may experience pain, soreness, and stiffness at the incision. Get up frequently (every 20 minutes) and move around or walk. Don’t sit or lie down for long periods of time.
Recurrences of neck pain are common. The key to avoiding recurrence is prevention:
What are the results?
Anterior cervical discectomy is successful in relieving arm pain in 92 to 100% of patients [3]. However, arm weakness and numbness may persist for weeks to months. Neck pain is relieved in 73 to 83% of patients [3]. In general, people with arm pain benefit more from ACDF than those with neck pain. Aim to keep a positive attitude and diligently perform your physical therapy exercises.
Achieving a spinal fusion varies depending on the technique used and your general health (smoker). In a study that compared three techniques: ACD, ACDF, and ACDF with plates and screws, the outcomes were [3]:
- 67% of people who underwent ACD (no bone graft) achieved fusion naturally. However, ACD alone results in an abnormal forward curving of the spine (kyphosis) compared with the other techniques.
- 93% of people who underwent ACDF with bone graft placement achieved fusion.
- 100% of people who underwent ACDF with bone graft placement and plates and screws achieved fusion.
What are the risks?
No surgery is without risks. General complications of any surgery include bleeding, infection, blood clots (deep vein thrombosis), and reactions to anesthesia. If spinal fusion is done at the same time as a discectomy, there is a greater risk of complications. Specific complications related to ACDF may include:
Hoarseness and swallowing difficulties. In some cases, temporary hoarseness can occur. The recurrent laryngeal nerve, which innervates the vocal cords, is affected during surgery. It may take several months for this nerve to recover. In rare cases (less than 1/250) hoarseness and swallowing problems may persist and need further treatment with an ear, nose and throat specialist.
Vertebrae failing to fuse. Among many reasons why vertebrae fail to fuse, common ones include smoking, osteoporosis, obesity, and malnutrition. Smoking is by far the greatest factor that can prevent fusion. Nicotine is a toxin that inhibits bone-growing cells. If you continue to smoke after your spinal surgery, you could undermine the fusion process.
Hardware fracture. Metal screws, rods, and plates used to stabilize the spine are called “hardware.” The hardware may move or break before your vertebrae are completely fused. If this occurs, a second surgery may be needed to fix or replace the hardware.
Bone graft migration. In rare cases (1 to 2%), the bone graft can move from the correct position between the vertebrae soon after surgery. This is more likely to occur if hardware (plates and screws) are not used to secure the bone graft. It’s also more likely to occur if multiple vertebral levels are fused. If this occurs, a second surgery may be necessary.
Transitional syndrome (adjacent-segment disease). This syndrome occurs when the vertebrae above or below a fusion take on extra stress. The added stress can eventually degenerate the adjacent vertebrae and cause pain.
Nerve damage or persistent pain. Any operation on the spine comes with the risk of damaging the nerves or spinal cord. Damage can cause numbness or even paralysis. However, the most common cause of persistent pain is nerve damage from the disc herniation itself. Some disc herniations may permanently damage a nerve making it unresponsive to decompressive surgery. In these cases, spinal cord stimulation or other treatments may provide relief. Be sure to go into surgery with realistic expectations about your pain. Discuss your expectations with your doctor.
Sources & links
If you have more questions, please contact the Call Us: (214) 396-3647 | (888) 373-3720
Fax #: (888)238-9155 | E-mail Us Come see on of our Doctors today please visit https://www.becomepainfree.com/
Sources
- Bose B: Anterior cervical instrumentation enhances fusion rates in multilevel reconstruction in smokers. J Spinal Disord 14:3-9, 2001.
- Hilibrand AS, et al.: Impact of smoking on the outcome of anterior cervical arthrodesis with interbody or strut-grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A:668-73, 2001.
- Xie JC, Hurlbert RJ. Discectomy versus discectomy with fusion versus discectomy with fusion and instrumentation: a prospective randomized study. Neurosurgery 61:107-16, 2007.
Links Come see on of our Doctors today please visit https://www.becomepainfree.com/
www.spine-health.com
www.spineuniverse.com
www.knowyourback.org
Glossary
annulus (annulus fibrosis): tough fibrous outer wall of an intervertebral disc.
fusion: to join together two separate bones into one to provide stability.
osteophytes: bony overgrowths that occur from stresses on bone, also called bone spurs.
Call Us: (214) 396-3647 | (888) 373-3720
Fax #: (888)238-9155 | E-mail Us
Come see on of our Doctors today please visit https://www.becomepainfree.com/